Bone grafting serves as a critical intervention in dental treatment, addressing bone loss in the jaw that can compromise tooth stability and facial structure. This procedure rebuilds the foundation necessary for dental implants, which are increasingly sought for their durability and natural appearance. The following insights explore its necessity, execution, and aftermath, emphasising practical steps for successful outcomes. By examining these elements, individuals can approach the process with clarity, ensuring alignment with broader goals in oral health maintenance.
One key consideration involves early assessment by specialists. Bone density diminishes due to factors such as periodontal disease, tooth extraction, or trauma, potentially leading to implant failure without intervention. Regular dental check-ups facilitate timely detection, preventing escalation. For those pursuing aesthetic enhancements, a cosmetic dentist London offers expertise in integrating grafting with restorative work, fostering confidence in treatment plans. This holistic approach underscores the procedure’s role in sustaining oral function amid daily routines.
The leading London cosmetic dentist from MaryleboneSmileClinic.co.uk emphasises the importance of personalised preparation: “Patients should discuss their medical history thoroughly to minimise risks, and incorporating anti-inflammatory measures pre-surgery can ease discomfort. For comprehensive resources on optimising your journey, visit this site.” Such guidance highlights the value of professional input, tailored to individual circumstances.
These insights proceed to detail the procedure’s facets, from graft selection to sustained healing, providing a structured pathway for patients navigating this essential dental advancement.
Determining When Bone Grafting is Necessary
Bone loss in the jawbone often goes unnoticed until it affects dental options, making grafting a pivotal step for restoration. This insight reveals that grafting becomes essential when imaging, such as panoramic X-rays or CT scans, indicates insufficient volume or density to support implants. In clinical practice, resorption occurs at a rate of up to 50 per cent in the first year post-extraction, accelerating with age or lifestyle factors like smoking. Recognising these signs early allows for proactive measures, preserving facial contours and bite alignment.
The diagnostic process begins with a thorough examination, where clinicians evaluate bone height, width, and quality. For instance, in the posterior mandible, inadequate bone can hinder implant placement, risking nerve proximity issues. Patients experiencing loose teeth, gum recession, or shifting bites should seek evaluation promptly. This not only averts further deterioration but also enhances the feasibility of cosmetic procedures, such as veneers or bridges, by ensuring a robust base.
Transitioning to candidacy, health status plays a decisive role. Conditions like uncontrolled diabetes or osteoporosis may necessitate modifications, yet advancements in materials mitigate many barriers. In London practices, where diverse patient profiles prevail, tailored assessments ensure suitability. This foundational insight equips individuals to identify triggers, prompting consultations that align grafting with long-term oral wellness.
Moreover, the interplay between bone health and overall vitality cannot be overstated. Adequate calcium intake and weight-bearing exercises support skeletal integrity, complementing clinical interventions. By understanding these prerequisites, patients contribute actively to their treatment trajectory, fostering outcomes that endure. This awareness transforms potential challenges into manageable steps, underscoring grafting’s role in comprehensive dental care.
Selecting the Appropriate Type of Graft
Choosing the right graft material marks a crucial insight, balancing efficacy with patient comfort. Autogenous grafts, harvested from the patient’s own body—typically the chin or hip—offer the highest integration rate due to living osteocytes, though they involve a secondary surgical site. Allografts, derived from human donors and sterilised, provide a viable alternative, eliminating additional harvesting while promoting osteoconduction through demineralised matrices.
Xenografts, sourced from bovine or porcine origins, serve as biocompatible scaffolds, resorbing gradually to encourage native bone formation. Their mineralised structure mimics human bone, reducing rejection risks. Alloplasts, synthetic options like hydroxyapatite or calcium phosphate, appeal for their availability and customisability, ideal for minor augmentations without biological sourcing concerns. Each type suits specific scenarios: autogenous for extensive defects, allografts for moderate needs.
Clinicians weigh factors such as defect size, healing timeline, and patient preferences during selection. For upper jaw sinus lifts, xenografts excel in volume retention, while alloplasts suit ridge preservations post-extraction. This decision influences recovery duration, with synthetics often accelerating initial stabilisation. In cosmetic contexts, material choice impacts aesthetic predictability, ensuring seamless implant integration.
Ethical and regulatory standards in the UK govern sourcing, with bodies like the Human Tissue Authority overseeing allografts to uphold safety. Patients benefit from informed discussions, aligning selections with lifestyle demands. This insight empowers proactive engagement, optimising graft performance and minimising interventions. Ultimately, the chosen material lays the groundwork for resilient bone regeneration, supporting enduring dental solutions.
Preparing for the Surgical Procedure
Preparation forms the third essential insight, streamlining the grafting experience through meticulous planning. Pre-operative consultations involve detailed health reviews, including medication adjustments—such as pausing blood thinners—and laboratory tests to confirm clotting proficiency. Smoking cessation, ideally four weeks prior, enhances vascularity, while a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D bolsters tissue repair capacity.
Anxiety management integrates via sedation options, from local anaesthesia to intravenous modalities, ensuring comfort without compromising safety. Patients receive custom mouthguards or stents to guide precise graft placement, reducing operative variability. Hydration protocols and fasting guidelines, typically six hours pre-surgery, safeguard procedural integrity. In London facilities, digital planning tools like 3D simulations preview outcomes, alleviating uncertainties.
This phase extends to logistical arrangements: arranging transport, as effects linger post-anaesthesia, and preparing a recovery space with soft pillows for elevation. Antimicrobial rinses commence days ahead, curbing bacterial load. For those combining with implants, staging decisions—grafting first for integration—prioritise stability. These steps mitigate intraoperative surprises, fostering efficiency.
Engaging family or support networks aids adherence, particularly for extended preps. This insight highlights preparation’s ripple effects, from smoother execution to expedited healing. By investing time upfront, patients not only enhance success rates but also cultivate resilience, viewing surgery as a controlled progression toward restored oral function.
Navigating the Immediate Aftermath
The immediate post-operative period demands vigilant care, encapsulating the fourth insight on managing initial responses. Swelling peaks within 48 hours, controlled by intermittent ice application—20 minutes on, 20 off—elevating the head during rest. Mild bleeding, normal for 24 hours, abates with gentle pressure via gauze; persistent oozing warrants contact with the practitioner.
Pain, typically moderate, responds to prescribed analgesics like paracetamol or ibuprofen, alternating for synergy. Antibiotics, if indicated, combat infection risks, taken as directed to maintain efficacy. Rest predominates the first day, avoiding exertion to preserve clot integrity. Oral hygiene shifts to saline rinses after 24 hours, sidestepping vigorous brushing near the site.
Dietary transitions favour cool, soft consistencies: smoothies, yoghurts, and mashed potatoes supply nutrients without mechanical stress. Hydration sustains via straw-free sipping, preventing dislodgement. Follow-up appointments, often within a week, monitor progress via clinical exams or radiographs. This phase, lasting 7-10 days, sets healing momentum.
Emotional adjustments, including brief fatigue, normalise with light activities resuming gradually. In urban environments, this downtime aligns with remote work trends, minimising disruption. This insight stresses adherence’s role in averting setbacks, transforming recovery’s onset into a structured, empowering interval.
Optimising Long-Term Recovery
Sustained healing constitutes the fifth insight, spanning months where lifestyle integration proves paramount. Bone integration, or osseointegration, unfolds over 3-6 months for most grafts, monitored through serial imaging to verify density gains. Gentle exercises, like jaw mobilisation, recommence per guidance, countering stiffness without overload.
Nutritional focus persists: protein sources—fish, eggs, legumes—fuel collagen synthesis, alongside calcium-rich dairy or fortified alternatives for mineralisation. Vitamin supplements, under supervision, address deficiencies, accelerating remodelling. Activity resumption follows a tiered approach: light walking by day three, full routines after two weeks, eschewing contact sports until cleared.
Oral care evolves with soft brushes and fluoride pastes, complemented by professional cleanings to forestall plaque accumulation. Stress management, via mindfulness or adequate sleep, influences inflammatory responses, aiding regeneration. For smokers resuming cautiously, nicotine patches offer harm reduction during critical windows.
This extended horizon rewards patience, with milestones like implant loading at six months yielding functional gains. In cosmetic pursuits, this period refines aesthetics, as restored volume enhances smile symmetry. This insight underscores proactive habits’ compounding benefits, ensuring grafts evolve into seamless skeletal components.
Mitigating Risks and Complications
Vigilance against complications forms the sixth insight, safeguarding graft viability through prevention. Infections, manifesting as fever or pus, arise in under 5 per cent of cases; prophylactic antibiotics and hygiene mitigate this. Graft rejection, rare with modern materials, signals via persistent pain—prompt intervention via debridement resolves most.
Nerve irritation, more common in mandibular sites, presents as numbness, resolving spontaneously in 80 per cent within weeks; steroids expedite if needed. Sinus perforations, in maxillary lifts, require membrane repairs to avert contamination. Swelling or haematoma, managed proactively, rarely escalates with elevation and compression.
Patient education empowers: recognising red flags like uncontrolled bleeding or allergic reactions enables swift action. Lifestyle abstentions—alcohol for 72 hours, straws indefinitely—curb pressures. Regular check-ins calibrate adjustments, leveraging technologies like platelet-rich plasma for enhanced biocompatibility.
In London’s regulatory framework, audited protocols minimise variances, bolstering confidence. This insight reframes risks as surmountable, emphasising collaboration. By prioritising these measures, patients not only avert disruptions but fortify trust in the process, yielding resilient results.
Enhancing Aesthetic Outcomes Through Integration
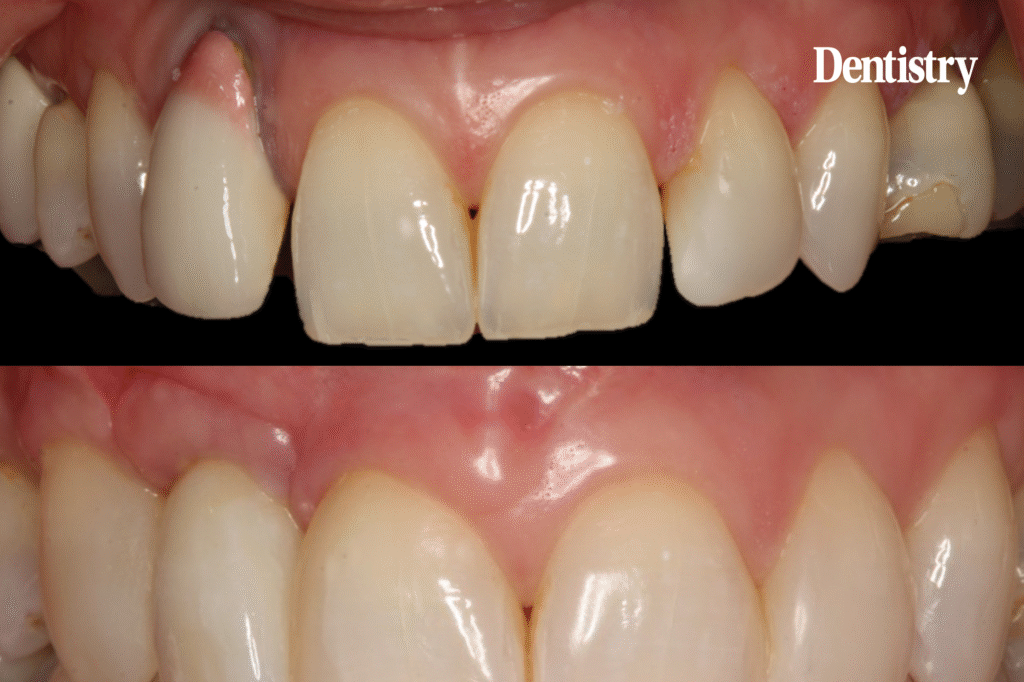
The seventh insight illuminates bone grafting’s synergy with cosmetic dentistry, elevating functional repairs to aesthetic triumphs. Restored volume prevents jowl sagging, harmonising facial proportions for a youthful profile. Implants anchored in grafted bone withstand occlusal forces, preserving veneer or crown alignments over decades.
In procedural fusion, simultaneous grafting during extractions streamlines timelines, reducing sessions. Materials like deproteinised xenografts blend imperceptibly, supporting porcelain fusions that mimic enamel translucency. Post-graft orthodontics corrects misalignments, unveiled through enhanced support.
Patient stories in UK clinics attest to transformations: renewed confidence from contiguous smiles, unmarred by gaps. A cosmetic dentist London, versed in interdisciplinary approaches, coordinates with periodontists for bespoke plans, incorporating digital mock-ups for preview.
Maintenance sustains these gains: biannual hygienist visits and night guards deter parafunctional wear. This integration not only amplifies visual appeal but embeds durability, aligning with holistic wellness. The eighth insight extends to economic prudence—grafting averts costlier revisions, with NHS options supplementing private enhancements where eligible.
Finally, the ninth insight celebrates innovation: stem cell-infused grafts and 3D-printed scaffolds promise abbreviated recoveries, customised via AI analytics. These frontiers, trialled in leading centres, herald accessible advancements. Collectively, these insights demystify bone grafting, positioning it as a versatile ally in dental evolution. Patients armed with this knowledge navigate recovery adeptly, realising smiles that endure and inspire.
